Semantic search
| Term | Abbreviation | Description | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference state | Z | The reference state Z (reference rate ZX) is the respiratory state with high flux in relation to the background state Y with low background flux YX. The transition between the background state and the reference state is a step brought about by a metabolic control variable X. If X stimulates flux (ADP, fuel substrate), it is present in the reference state but absent in the background state. If X is an inhibitor of flux, it is absent in the reference state but present in the background state. The reference state is specific for a single step to define the flux control efficiency. In contrast, in a sequence of multiple steps, the common reference state is frequently taken as the state with the highest flux in the entire sequence, as used in the definition of the flux control ratio. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference-Electrode\2.4 mm | Reference-Electrode\2.4 mm: 2.4 mm diameter glass shaft, for ISE. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References in BEC https-format | BEC https-format | References in BEC https-format show (1) the list of authors, (2) the year of publication in parentheses, (3) the title of the publication, and (4) the https://doi.org/ link. Removing all the unnecessary detail of journal name and pages, the focus is on authors, year, and title of the reference, which is a concept in line with DORA. The https-link then does the full job. In exceptional cases when there is no such link, the following formats would apply: a https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ link, a link directly to an Open Access pdf, or the old conventional format for the reference. Scientific journals apply yesterday's concepts in the various formats of references with bewildering abbreviations of journals, volumes, issues, page numbers. We can do today's job much better using the BEC https-format:
Compare with a conventional reference format in: Gnaiger E (2021) Beyond counting papers – a mission and vision for scientific publication. https://doi.org/10.26124/bec:2021-0005 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reflectance spectrophotometry | In reflectance spectrophotometry the light from the sample is reflected back to the detector using mirrors. Before absorbance measurements can be made, a white balance is carried out. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reliability | Reliability relates the magnitude of the measurement error in observed measurements (i.e., precision or intermediate precision) to the inherent variability in the ‘error-free’, ‘true’, or underlying level of the quantity between subjects. The value of the reliability takes a value between 0 and 1. When the variability value is zero, indicates that all the variability in the measurements is due to measurement error. And, on the contrary, when the value is 1 indicates that there is a zero error in the measurement error. It is also known as the intraclass correlation, as it equals the correlation between any two measurements made on the same subject. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Remittance spectrophotometry | In remittance spectrophotometry incident light enters a scattering medium and is scattered back to the receiving optics (usually lightguides) before being directed to the detector. Before absorbance measurements can be made, a white balance is carried out. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repetitions | n | Repetitions of an experiment or assay are designed to obtain statistical information on the methodological precision of the measurements. A number of repetitions, n, of measurements are performed on the same sample, applying an identical experimental protocol to subsamples, without providing any information on variability between samples. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Replacement-Barrel | Replacement-Barrel for Reference-Electrode\2.4 mm, 2.4 mm diameter glass. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Replica | N | Replica are designed in scientific studies to evaluate the effect of uncontrolled variability on a result obtained from an experiment on a single sample, to describe the variability and distribution of experimental results, and to obtain statistical information such as the median or average for a defined sample size. It may be useful to make a terminological distinction between replica of experiments, N, designed to obtain statistical information on the population, and repetitions of experiments or assays, n, designed to obtain statistical information on the methodological precision of the measurements. The terms study, experiment and assay have to be defined carefully in this context. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reproducibility crisis | The reproducibility crisis is alarming.1 An experiment or study is reproducible or replicable when subsequent experiments confirm the results. This is re-search. However, we can define different types of reproducibility depending on the conditions that we use to replicate the previous work or in the information available. Our aim is to focus mostly on two different kinds2: 1. Direct: is when we obtaining the same results using the same experimental conditions, materials, and methods as described in the original experiment. This would be the ideal reproducibility of an experiment. However, it requires a very accurate description of how the original experiment was performed. Some journals are trying to resolve the reproducibility crisis improving the rigor and the excellence on the reported methods and results (e.g. STAR Methods in Cell Press). 2. Systematical: refers to obtaining the same results, but under different conditions; for example, using another cell line or mouse strain or humman study, or inhibiting a gene pharmacologically instead of genetically. This opens the door to subsequent studies to find the conditions under which an initial finding holds. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Requirement | A requirement is a singular documented physical or functional need that a particular design, product or process must be able to perform. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research | Research is a term composed of search and re. What does this tell us? The best comparison of the English with a German word is Untersuchung, composed of suchung (search) and unter (below). The term search (suchen) is straightforward to understand and comparable in both languages. The prefix re and unter are more difficult to reconcile, yet in both languages these perfixes reveal complementary if not nearly identical messages. re means {Quote} back to the original place; again, anew, once more {end of Quote} [1], whereas unter means below or underneath. Re-search, therefore, is not simply the search or investigation of some topic or problem, it means essentially doing the search again and again (re -> re-producibility) and penetrating below a simple search by reaching out for an underlying level of the search. The re in re-search and re-producibility has to be extended ultimately from a single re-search group to inter-laboratory re-investigation. This tells us, therefore, that while search is valuable, re-search provides the necessary validation. This re-evaluation of confirmative re-search should be re-cognized as the most important strategy to address the reproducibility crisis. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Residual endogenous substrates | REN, Ren |
Ren may be higher than Rox. Correspondingly, Q and NAD are not fully oxidized in the REN state compared to the ROX state. In previous editions (including Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways), the REN state was not distinguished from the ROX state. However, in novel applications (Q-Module and NADH-Module), a distinction of these states is necessary. Care must be taken when assuming Ren as a substitute of Rox correction of mitochondrial respiration. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Residual oxygen consumption | ROX, Rox |
In previous editions, (including Gnaiger 2020 BEC MitoPathways), the REN state was not distinguished from the ROX state. However, in novel applications (Q-Module and NADH-Module), a distinction of these states is necessary. Care must be taken when assuming Ren as a substitute of Rox correction of mitochondrial respiration. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resolution | Spectral resolution is a measure of the ability of an instrument to differentiate between two adjacent wavelengths. Two wavelengths are normally considered to be resolved if the minimum detector output signal (trough) between the two peaks is lower than 80 % of the maximum. The resolution of a spectrofluorometer or spectrophotometer is dependent on its bandwidth. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resorufin | Res | Resorufin is a fluorescence probe used in various biological assays. Among others, it is the product obtained in the Horseradish peroxidase-catalyzed assay using Amplex Red for the measurement of H2O2 production. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory acceptor control ratio | RCR | The respiratory acceptor control ratio (RCR) is defined as State 3/State 4 [1]. If State 3 is measured at saturating [ADP], RCR is the inverse of the OXPHOS control ratio, L/P (when State 3 is equivalent to the OXPHOS state, P). RCR is directly but non-linearly related to the P-L control efficiency, jP-L = 1-L/P, with boundaries from 0.0 to 1.0. In contrast, RCR ranges from 1.0 to infinity, which needs to be considered when performing statistical analyses. In living cells, the term RCR has been used for the ratio State 3u/State 4o, i.e. for the inverse L/E ratio [2,3]. Then for conceptual and statistical reasons, RCR should be replaced by the E-L coupling efficiency, 1-L/E [4]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory chain | RC | The mitochondrial respiratory chain (RC) consists of enzyme complexes arranged to form a metabolic system of convergent pathways for oxidative phosphorylation. In a general sense, the RC includes (1) the electron transfer pathway (ET-pathway), with transporters for the exchange of reduced substrates across the inner mitochondrial membrane, enzymes in the matrix space (particularly dehydrogenases of the tricarboxylic acid cycle), inner membrane-bound electron transfer complexes, and (2) the inner membrane-bound enzymes of the phosphorylation system. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory complexes | CI, CII, CIII, CIV, CETF, CGpDH, .. | Respiratory Complexes are membrane-bound enzymes consisting of several subunits which are involved in energy transduction of the respiratory system. » MiPNet article | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respiratory state | Respiratory states of mitochondrial preparations and living cells are defined in the current literature in many ways and with a diversity of terms. Mitochondrial respiratory states must be defined in terms of both, the coupling-control state and the electron-transfer-pathway state. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Respirometry | Respirometry is the quantitative measurement of respiration. Respiration is therefore a combustion, a very slow one to be precise (Lavoisier and Laplace 1783). Thus the basic idea of using calorimetry to explore the sources and dynamics of heat changes were present in the origins of bioenergetics (Gnaiger 1983). Respirometry provides an indirect calorimetric approach to the measurement of metabolic heat changes, by measuring oxygen uptake (and carbon dioxide production and nitrogen excretion in the form of ammonia, urea, or uric acid) and converting the oxygen consumed into an enthalpy change, using the oxycaloric equivalent. Liebig (1842) showed that the substrate of oxidative respiration was protein, carbohydrates, and fat. The sum of these chemical changes of materials under the influence of living cells is known as metabolism (Lusk 1928). The amount (volume STP) of carbon dioxide expired to the amount (volume STP) of oxygen inspired simultaneously is the respiratory quotient, which is 1.0 for the combustion of carbohydrate, but less for lipid and protein. Voit (1901) summarized early respirometric studies carried out by the Munich school on patients and healthy controls, concluding that the metabolism in the body was not proportional to the combustibility of the substances outside the body, but that protein, which burns with difficulty outside, metabolizes with the greatest ease, then carbohydrates, while fats, which readily burns outside, is the most difficultly combustible in the organism. Extending these conclusions on the sources of metabolic heat changes, the corresponding dynamics or respiratory control was summarized (Lusk 1928): The absorption of oxygen does not cause metabolism, but rather the amount of the metabolism determines the amount of oxygen to be absorbed. .. metabolism regulates the respiration. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resting metabolic rate | RMR | Resting respiration or resting metabolic rate (RMR) is measured under standard conditions of an 8–12-h fast and a 12-h abstinence from exercise. In an exemplary study (Haugen 2003 Am J Clin Nutr), "subjects rested quietly in the supine position in an isolated room with the temperature controlled to 21–24° C. RMR was measured for 15–20 min. Criteria for a valid RMR was a minimum of 15 min of steady state, determined as a <10% fluctuation in oxygen consumption and <5% fluctuation in respiratory quotient". The main difference between RMR and BMR (basal metabolic rate) is the position of the subject during measurement. Resting metabolic rate is the largest component of the daily energy budget in most human societies and increases with physical training state (Speakman 2003 Proc Nutr Soc). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Restore points | Select Restore points in the Mark information window to restore data points in the marked section of the active signal plot, if Delete points or Interpolate points was used before. Compare Recalculate slope. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Resveratrol | Resveratrol is a natural bioactive phenol prouced by several plants with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects. Dietary intake as nutraceutical is discussed for targeting mitochondria with a wide spectrum of action in degenerative diseases. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reverse electron flow from CII to CI | RET | Reverse electron flow from CII to CI stimulates production of ROS when mitochondria are incubated with succinate without rotenone in the LEAK state at a high mt-membrane potential. Depolarisation of the mt-membrane potential (e.g. after ADP addition to stimulate OXPHOS) leads to inhibition of RET and therefore, decrease of RET-initiated ROS production. RET can be also measured when mitochondria are respiring using Gp without rotenone in the LEAK state. Addition of IQ-side inhibitors (ubiquinone-binding side of CI) of CI usually block RET. The following SUIT protocols allow you to measure RET-initiated H2O2 flux in mitochondrial preparations: SUIT-009 and SUIT-026. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rhodamine 123 | Rh123 | Rhodamine 123 (Rh123) is an extrinsic fluorophore and can be used as a probe to determine changes in mitochondrial membrane potential. Rh123 is a lipophilic cation that is accumulated by mitochondria in proportion to Δψmt. Using ethanol as the solvent, the excitation maximum is 511 nm and the emission maximum is 534 nm. The recommended excitation and emission wavelengths in PBS are 488 and 515-575 nm, respectively (Sigma-Aldrich). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Risk management | Risk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Romero-Corral 2008 Int J Obes (Lond) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotenone | Rot | Rotenone is an inhibitor of Complex I (CI) and thus inhibits NADH oxidation. It inhibits the transfer of electrons from iron-sulfur clusters in CI to ubiquinone via binding to the ubiquinone binding site of CI. See also Succinate pathway. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Run DL-Protocol/Set O2 limit | DL-Protocols (DLP) can be selected in DatLab 7 in the pull-down menu 'Protocol': Set DL-Protocol / O2 limit. A DL-Protocol defines the sequence of Events and Marks and can be assigned to O2k-Chamber A or B, or both. Linked to DL-Protocols are templates for storing exported data in a database and for data analysis. Instrumental DL-Protocols are used for calibrations and instrumental quality control, without experimental sample in the incubation medium. DL-Protocols for substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) provide a guide through a sequence of coupling-control states and Electron-transfer-pathway states. A library of evaluated and tested standard DL-Protocols is provided by the Oroboros team. The Titration-Injection-microPump TIP2k can be programmed for automatic control of titration steps in a DL-Protocol. In DatLab 7.4, it is possible to edit a DL-Protocol and save it as a user-specific DL-Protocol (*.DLPU). For more information, see: Enable DL-Protocol editing. A Lower O2 limit [µM] can be defined for each chamber, to trigger an automatic warning when the experimental O2 concentration declines below this limit as a WARNING to remind the user that re-oxygenation of the medium may be required. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ruthenium red | RR | Ruthenium red (synonym: ammoniated ruthenium oxychloride) inhibits the mitochondrial Ca2+ uniporter. However, in addition it has been shown to interact with and inhibit a large number of other proteins, including ion channels particularly of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid (TRPV) family [1], Ca2+-ATPases, and, importantly, the voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) [2]. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| S/NS pathway control ratio | S/NS | The S/NS pathway control ratio is obtained when rotenone (Rot) is added to the NS-pathway control state in a defined coupling control state. The reversed protocol, adding N-type substrates to a S-pathway control state as the background state does not provide a valid estimation of S-linked respiration with succinate in the absence of Rot, since oxaloacetate accumulates as a potent inhibitor of succinate dehydrogenase (CII). | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SF6847 | SF6847 | SF6847 (C18H22N2O), also known as tyrphostin A9 or malonoben, is a protonophore and a very potent uncoupler of oxidative phosphorylation, being used in the nM range. Like all uncouplers, SF6847 concentrations must be titrated carefully to evaluate the optimum concentration for maximum stimulation of mitochondrial respiration, particularly to avoid inhibition of respiration at higher concentrations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SGp-pathway control state | SGp | SGp: Succinate & Glycerophosphate. MitoPathway control state: SGp; obtained with OctPGMSGp(Rot) SUIT protocol: SUIT-001 and ((SUIT-002 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI base units | Template:Keywords: SI base units
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SI prefixes | There are 20 SI prefixes defined to represent multiples and submiltiples of SI units. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| STPD | STPD | At standard temperature and pressure dry (STPD: 0 °C = 273.15 K and 1 atm = 101.325 kPa = 760 mmHg), the molar volume of an ideal gas, Vm, and Vm,O2 is 22.414 and 22.392 L∙mol-1, respectively. Rounded to three decimal places, both values yield the conversion factor of 0.744 from units used in spiroergometry (VO2max [mL O2·min-1]) to SI units [µmol O2·s-1]. For comparison at normal temperature and pressure dry (NTPD: 20 °C), Vm,O2 is 24.038 L∙mol-1. Note that the SI standard pressure is 100 kPa, which corresponds to the standard molar volume of an ideal gas of 22.711 L∙mol-1 and 22.689 L∙mol-1 for O2. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
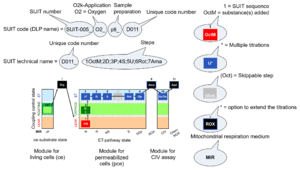
| SUIT | SUIT | SUIT is the abbreviation for Substrate-Uncoupler-Inhibitor Titration. SUIT protocols are used with mt-preparations to study respiratory control in a sequence of coupling and pathway control states induced by multiple titrations within a single experimental assay. These studies use biological samples economically to gain maximum information with a minimum amount of cells or tissue. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT protocol library | SUITs | The Substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocol library contains a sequential list of SUIT protocols (D001, D002, ..) with links to the specific SUIT pages. Classes of SUIT protocols are explained with coupling and substrate control defined for mitochondrial preparations. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT protocol names | SUITp-Names |
The SUIT protocol name starts with (i) the SUIT category which shows the Electron-transfer-pathway states (ET pathway types; e.g. N, S, NS, FNS, FNSGp), independent of the actual sequence of titrations. (ii) A further distinction is provided in the SUIT name by listing in parentheses the substrates applied in the N-pathway control states, again independent of the sequence of titrations, e.g. NS(GM), NS(PM), FNSGp(PGM). (iii) A sequentially selected number is added, e.g. SUIT_FNS(PM)01 (see Coupling/pathway control diagram). The systematic name of a SUIT protocol starts with the SUIT category, followed by an underline dash and the sequence of titration steps (mark names, #X, separated by a comma). The Marks define the section of a respiratory state in the SUIT protocol. The Mark name contains the sequential number and the metabolic control variable, X. The metabolic control variable is the name of the preceding SUIT event. The MitoPedia list of SUIT protocols can be sorted by the short name or the systematic name (hence by SUIT protocol category. The SUIT protocol pattern is best illustrated by a coupling/pathway control diagram. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT protocol pattern | SUITp-Pattern | The SUIT protocol pattern describes the type of the sequence of coupling and substrate control steps in a SUIT protocol, which may be liner, orthogonal, or diametral. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT reference protocol | SUIT RP | The substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) reference protocol, SUIT RP, provides a common baseline for comparison of mitochondrial respiratory control in a large variety of species, tissues and cell types, mt-preparations and laboratories, for establishing a database on comparative mitochondrial phyisology. The SUIT RP consists of two harmonized SUIT protocols (SUIT-001 - RP1 and SUIT-002 - RP2). These are coordinated such that they can be statistically evaluated as replicate measurements of cross-linked respiratory states, while additional information is obtained when the two protocols are conducted in parallel. Therefore, these harmonized SUIT protocols are complementary with their focus on specific respiratory coupling and pathway control aspects, extending previous strategies for respirometrc OXPHOS analysis.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-001 | RP1 | 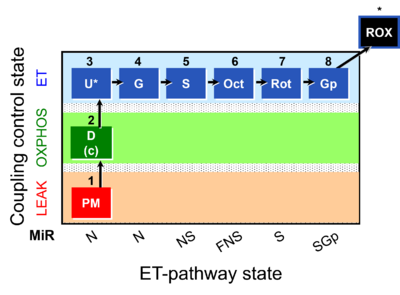 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-001 O2 ce-pce D003 | RP1 ce-pce | 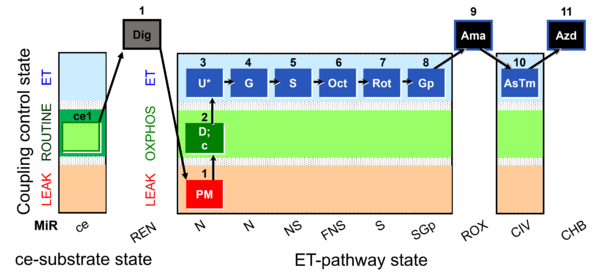 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-001 O2 ce-pce D004 | RP1 ce-pce blood | 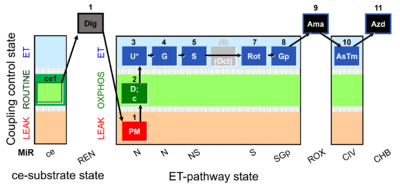 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-001 O2 mt D001 | RP1 mt | 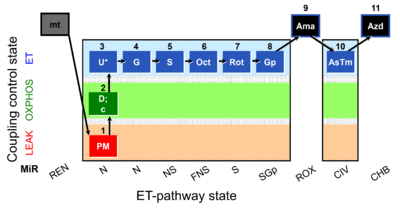 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-001 O2 pfi D002 | RP1 pfi | 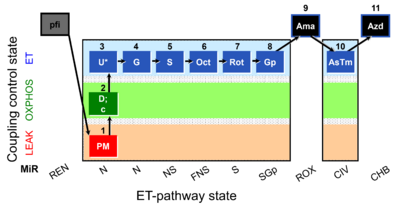 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-002 | RP2 | 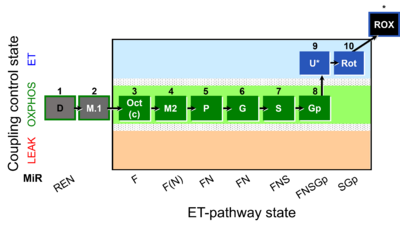 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-002 O2 ce-pce D007 | RP2 ce-pce | 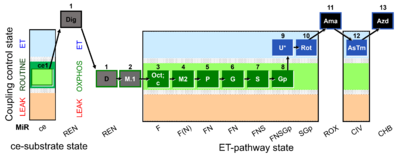 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-002 O2 ce-pce D007a | RP2 ce-pce blood |  | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-002 O2 mt D005 | RP2 mt | 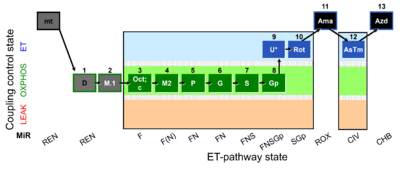 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-002 O2 pfi D006 | RP2 pfi | 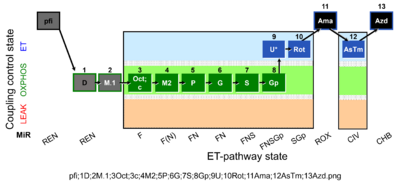 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 | CCP-ce | 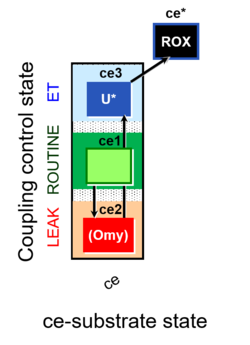 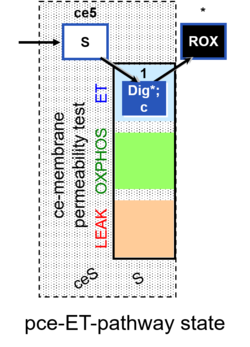 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 AmR ce D017 | CCP-ce S permeability test | 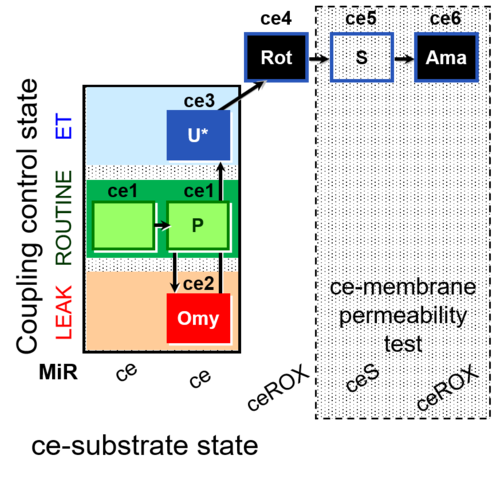 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 AmR ce D058 | AmR effect on ce | 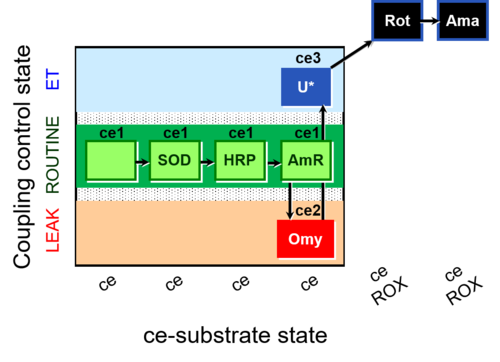 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 AmR ce D059 | AmR effect on ce - control | 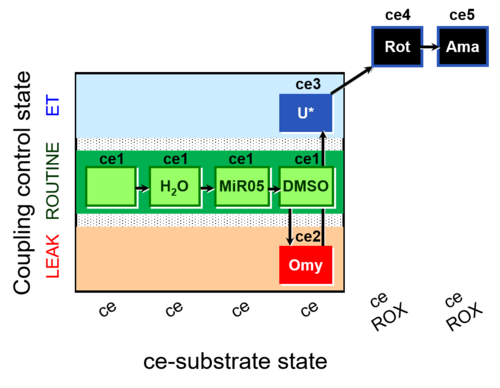 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce1P;ce3U;ce4Glc;ce5M;ce6Rot;ce7S;1Dig;1c;2Ama;3AsTm;4Azd | cePMGlc,S | 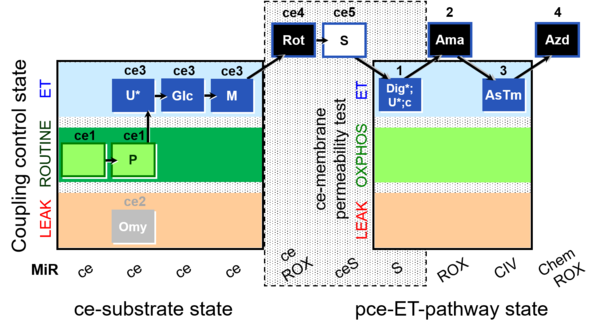 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce1SD;ce2Omy;ce3U- | FNS(Oct,PGM) | 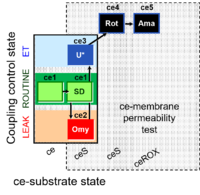 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce1SD;ce3U;ce4Rot;ce5Ama | ceS | 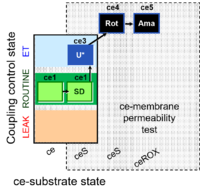 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce2SD;ce3Omy;ce4U- | FNS(Oct,PGM) | 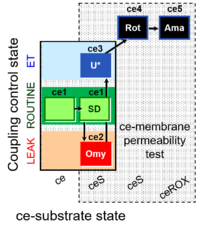 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce2SD;ce3U;ce4Rot;ce5Ama | ceS | 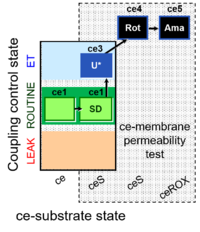 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce2U;ce3Rot;ce4S;ce5Ama | ceS | 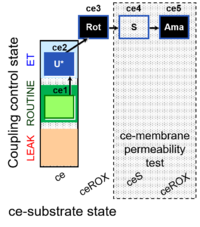 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce2U- | ce | 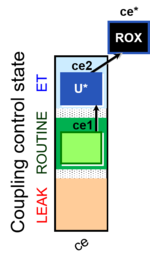 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce3U;ce4Rot;ce5S;ce6Ama | ceS | 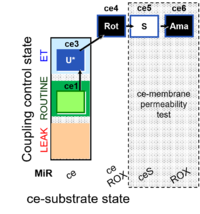 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 Ce1;ce3U- | ce | 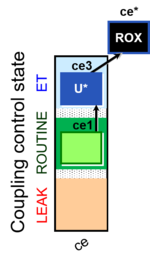 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D009 | CCP-ce short | 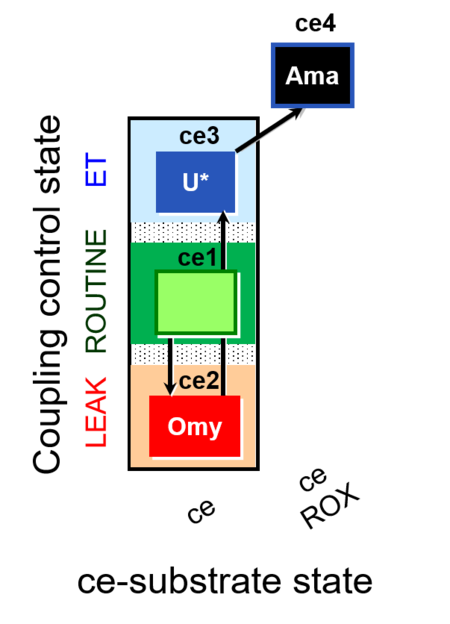 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D012 | CCP-ce(P) | 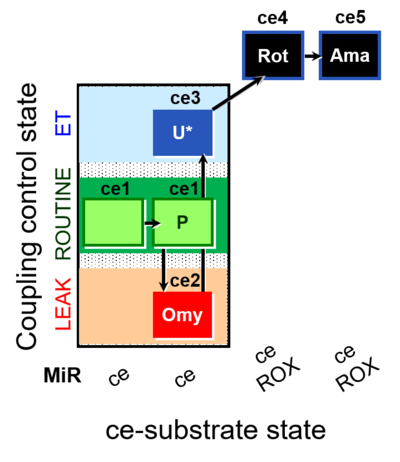 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D028 | CCP-ce S permeability test | 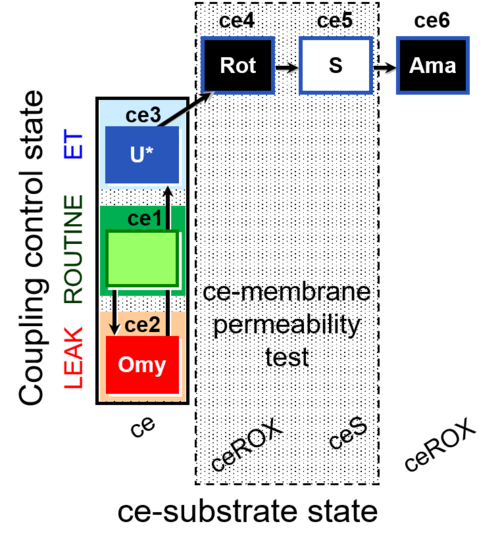 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D037 | CCP-ce Crabtree_R | 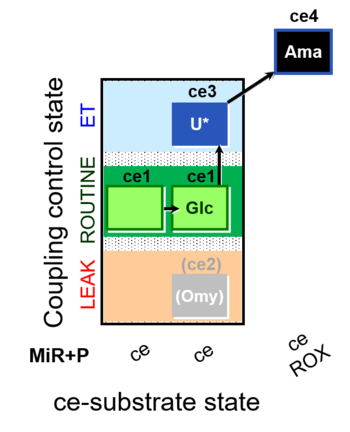 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D038 | CCP-ce Crabtree_E | 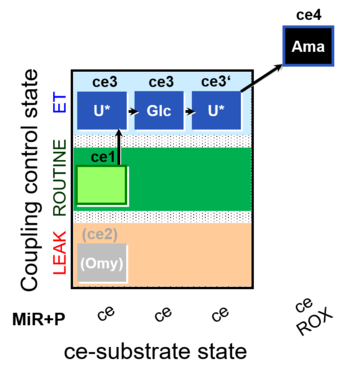 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D039 | CCP-ce microalgae | 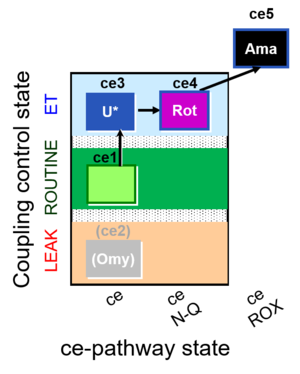 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D050 | CCP-ce Snv | 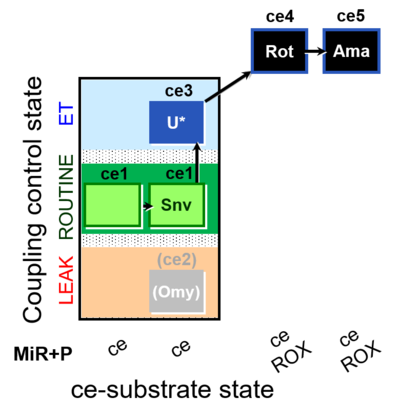 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D060 | CCP-ce Snv,Mnanv | 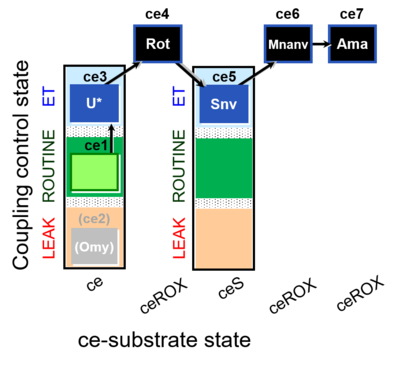 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D061 | CCP-ce Snv,Mnanv - control | 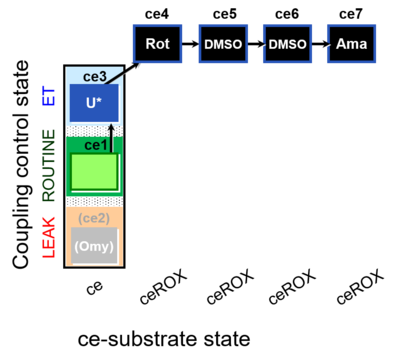 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce D062 | CCP-ce Snv - control | 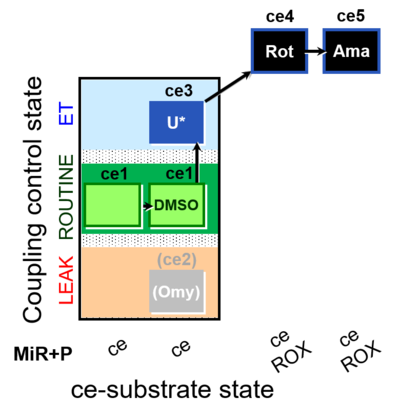 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce-pce D013 | CCVP-Glc,M | 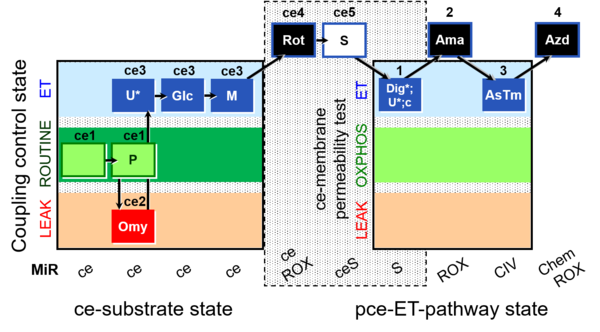 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce-pce D018 | CCVP-Glc | 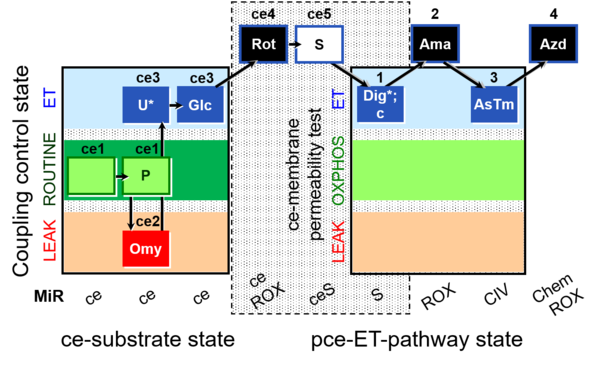 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 O2 ce-pce D020 | CCVP | 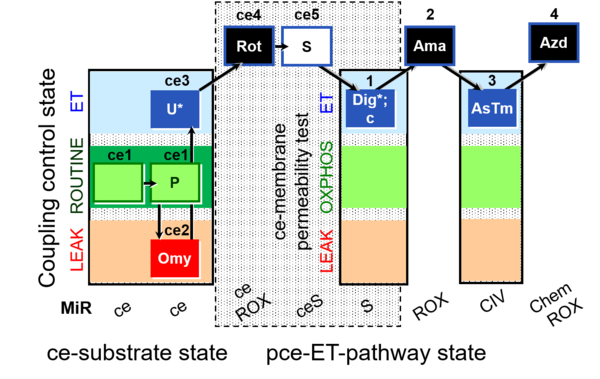 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-003 pH ce D067 | CCP-Crabtree with glycolysis inhibition | 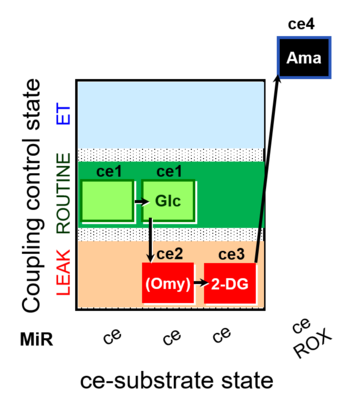 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-004 | RP1-short | 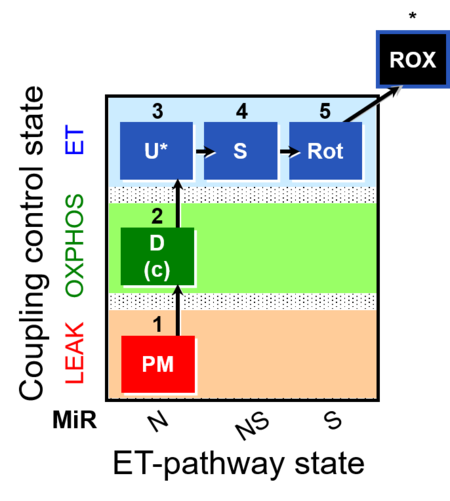 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-004 O2 pfi D010 | RP1-short pfi | 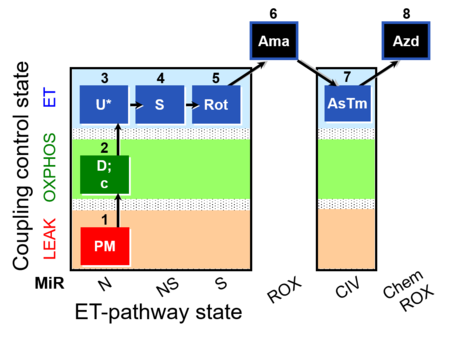 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-005 | RP2-short | 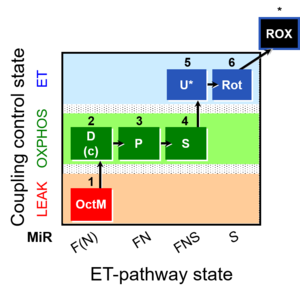 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-005 O2 pfi D011 | RP2-short pfi | 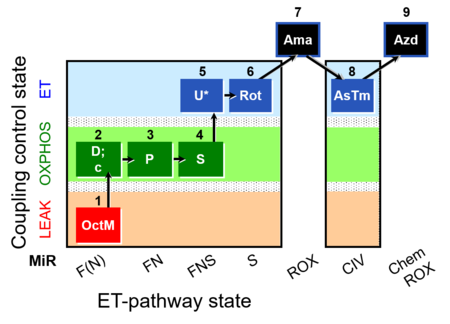 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 | CCP-mtprep | 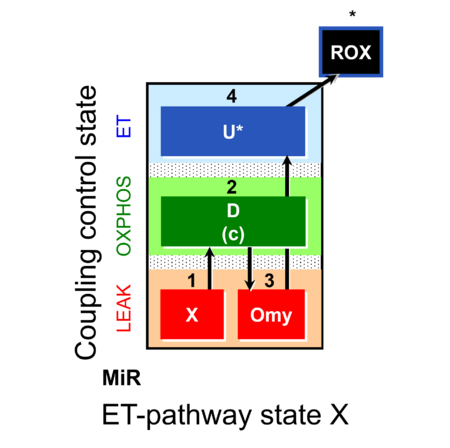 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 02 mt D108 | 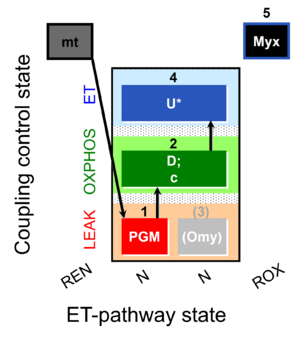 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 AmR mt D048 | CCP mt PM - AmR | 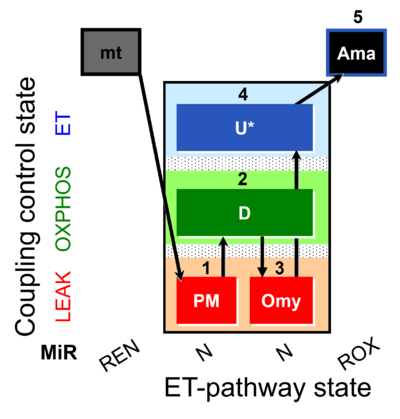 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 Fluo mt D034 | CCP mt PM - Fluo | 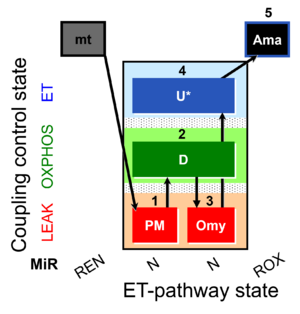 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 MgG ce-pce D085 | CCP MgG ce-pce | 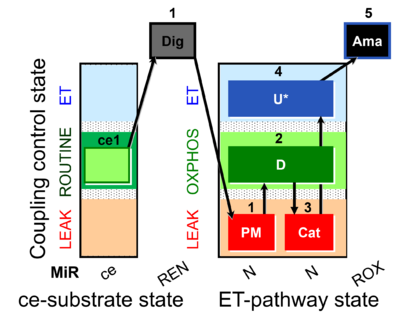 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 MgG mt D055 | CCP MgG mt | 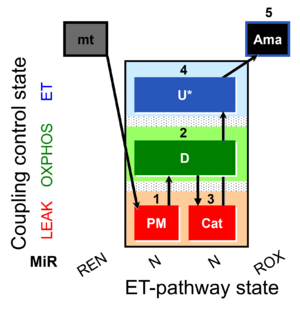 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 NADH mt D084 | 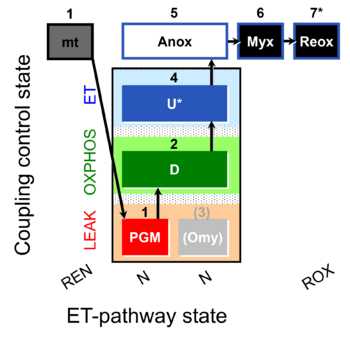 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 O2 ce-pce D029 | CCP ce-pce PM | 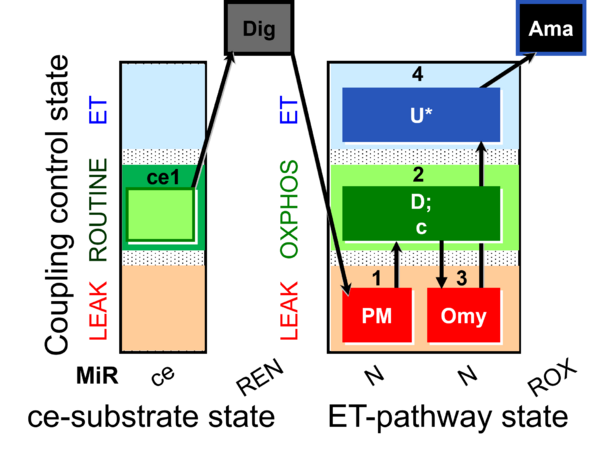 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 O2 mt D022 | CCP mt S(Rot) | 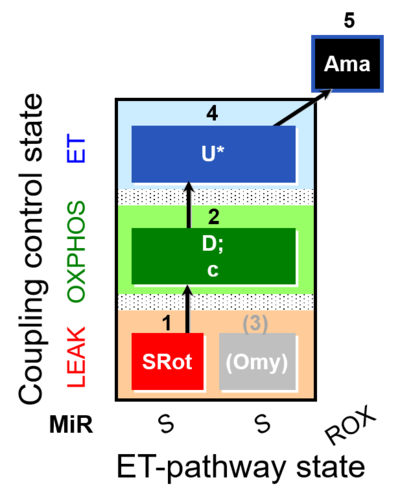 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 O2 mt D047 | CCP mt PM | 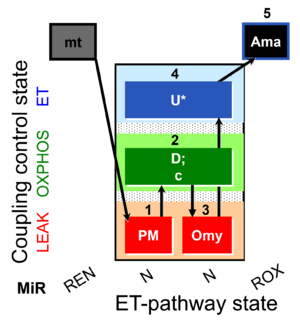 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 Q ce-pce D073 | CCP ce-pce S(Rot) | 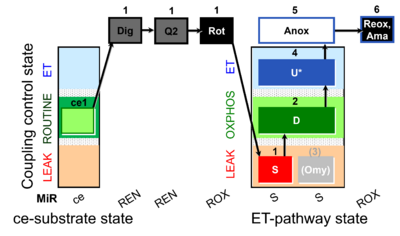 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-006 Q mt D071 | CCP mt S(Rot) | 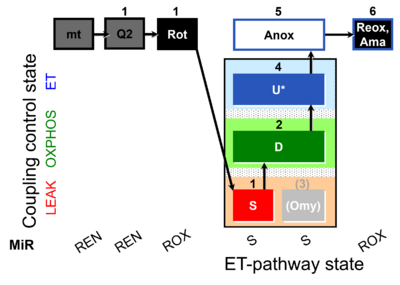 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-007 | Glutamate anaplerosis | 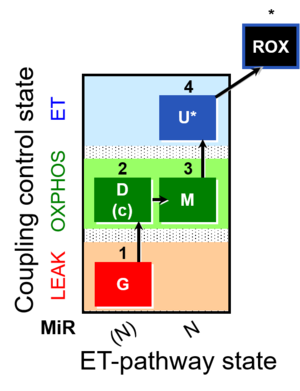 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-007 O2 ce-pce D030 | Glutamate anaplerotic pathway | 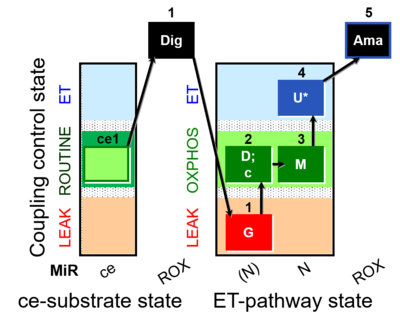 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-008 | PM+G+S_OXPHOS+Rot_ET | 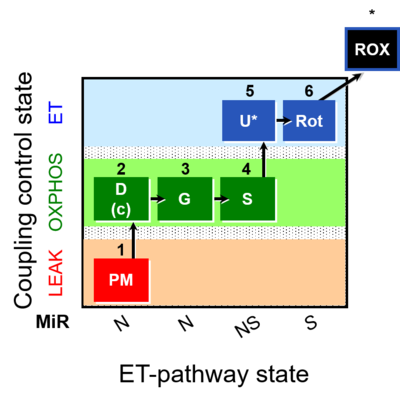 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-008 O2 ce-pce D025 | Q-junction ce-pce | 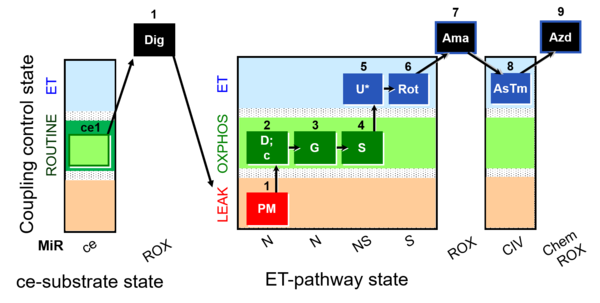 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SUIT-008 O2 mt D026 | Q-junction mtprep | 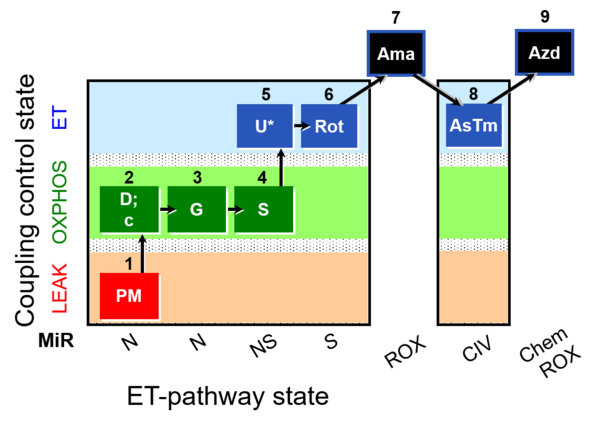 |