Difference between revisions of "Superoxide dismutase"
From Bioblast
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
|mitopedia topic=Enzyme | |mitopedia topic=Enzyme | ||
}} | }} | ||
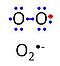
[[File:O2-.jpg|right|60px|Superoxide anion]] | |||
== Application in [[fluorometry]] == | == Application in [[fluorometry]] == | ||
* Add SOD for [[Amplex_red | measurement of H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> with Amplex Red]]. | * Add SOD for conversion of O<sub>2</sub><sup>•-</sup> and [[Amplex_red | measurement of H<sub>2</sub>O<sub>2</sub> with Amplex Red]]. | ||
Revision as of 03:48, 16 April 2014
Description
Mammalian superoxide dismutase (SOD) exists in three forms, of which the Mn-SOD occurs in mitochondria (mtSOD, SOD2; 93 kD homotetramer) and many bacteria, in contrast to the Cu-Zn forms of SOD (cytosolic SOD1, extracellular SOD3 anchored to the extracellular matrix and cell surface). Superoxide anion (O2•-) is a major reactive oxygen species (ROS) which is dismutated by SOD to oxygen and H2O2.
Abbreviation: SOD
Reference: Fridovich_1997_J Biol Chem
MitoPedia topics: Enzyme
Application in fluorometry
- Add SOD for conversion of O2•- and measurement of H2O2 with Amplex Red.