From Bioblast
Description
Abbreviation: QC_imt_PM_T+OXPHOS+c+Omy_ET_G+S+Rot
Reference: A: quality control evaluation of mitochondrial preparations - SUIT-029
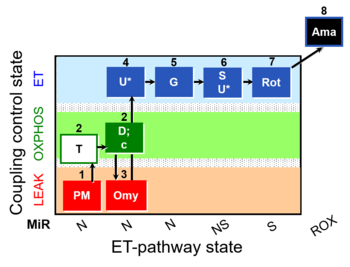
SUIT number: D066_mt;1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot;8Ama
O2k-Application: O2
- MitoPedia: SUIT
- SUIT protocol pattern: mt;1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot;-
- The SUIT-029 O2 mt D066 is designed to evaluate the quality control of mitochondrial preparation. This protocol gives information of the linear coupling control (L- P- E) with NADH linked-substrates (PM). SUIT-029 O2 mt D066 includes a control for contamination with other organelles containing ATPases (e.g., plasma membrane and endoplasmic reticulum.) In experiments with crude isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenates and permeabilized cells, it is expected to have active ATPases in the preparation. When ATPases are active, residual endogenous adenylates are phosphorylated to ATP in the LEAK state, which is recycled to ADP in isolated mitochondria contaminated by ATPases, which leads to an overestimation of LEAK respiration, when comparing L(n) and L(Omy). Therefore, it might be necessary to assess LEAK respiration in the presence of ATPase inhibitors, e.g. oligomycin. Additive effect of convergent electron flow through NADH- and NS-pathways is evaluated in the ET state.
- The present SUIT-029 O2 mt D066 DLP file shows an application with imt, thom or pce in the pathway category NS. For using this protocol with other mitochondrial preparations or substrate/inhibitor combinations, a personalized DLPU can be created.
Communicated by Antunes D, Komlodi T, Gnaiger E (last update 2020-05-12)
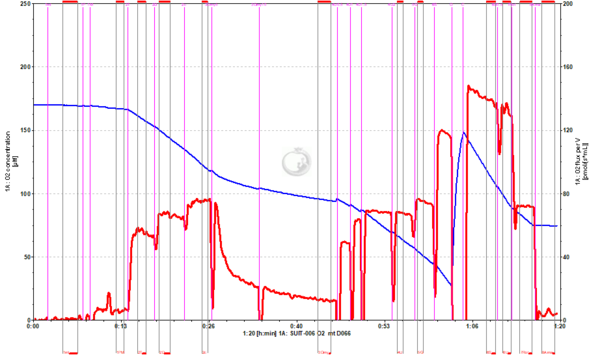
Representative traces
Steps and respiratory states
| Step | State | Pathway | Q-junction | Comment - Events (E) and Marks (M)
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1PM | PML(n) | N | CI | 1PM
|
| 2T | PML or PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T
|
| 2D | PMP | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D
|
| 2c | PMcP | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c
|
| 3Omy | PMLOmy | N | CI | 1PM;2D;2c;3Omy
|
| 4U | PME | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U
|
| 5G | PGME | N | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G
|
| 6S | PGMSE | NS | CI+CII | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S
|
| 6U | PGMSE | NS | CI+CII | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U
|
| 7Rot | SE | S | CI | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot
|
| 8Ama | ROX | 1PM;2T;2D;2c;3Omy;4U;5G;6S;6U;7Rot;8Ama
|
- Bioblast links: SUIT protocols - >>>>>>> - Click on [Expand] or [Collapse] - >>>>>>>
- Coupling control
- Pathway control
- Main fuel substrates
- » Glutamate, G
- » Glycerophosphate, Gp
- » Malate, M
- » Octanoylcarnitine, Oct
- » Pyruvate, P
- » Succinate, S
- Main fuel substrates
- Glossary
Strengths and limitations
- This protocol allows to evaluate the quality of mitochondrial preparations taking into account the presence of ATPases.
- + PM is the superior alternative to GM: with GM the fraction of the N-pathway is lower and S-pathway contribution is higher compared to PM. PM, therefore, yields a more sensitive assay for the diagnosis of injuries in the N-pathway, since in the case of GM impairment N-pathway capacity can be compensated partially by activation of the S-pathway.
- + Evaluation of the ATPase contamination is included (2T).
- + Integrity of mitochondrial outer membrane is assessed ( 2c).
- + Overestimation of LEAK respiration is prevented in the presence of Oligomycin as a control with the L(n) previously obtained.
- + Evaluation of ET-state with NADH-linked substrates allows to calculate ET-coupling efficiency (1-L/E).
- + The additive effect of convergent flux through NADH-linked respiration in the ET-state is evaluated (5G).
- + ET-state with NS-linked substrates is evaluated (5S) followed by additional U titration to ensure ET capacity.
- + Assessment of ET capacity not only in N- and NS-pathway but also in S-pathway (7Rot).
- + This protocol can be optionally harmonized with many other SUIT protocols (e.g., SUIT-001, SUIT-004, SUIT-008). Addition of G in NADH-linked OXPHOS enables evaluation of the glutamate-anaplerotic pathway control state.
- + This protocol can be extended with the Complex IV module.
- - Long duration of the experiment due to adjustment of Oligomycin concentration (in the case of a new isolation protocol). For a shorter protocol the titration of glutamate, succinate and rotenone could be omitted.
- - The use of Oligomycin could affect the evaluation of the ET capacity (could inhibit ET-state).
- - F-pathway is not analysed.
- - Careful washing is required after the experiment to avoid carry-over of inhibitors and uncoupler.
Compare SUIT protocols
- SUIT-001 (RP1): Harmonized SUIT protocol for isolated mitochondria, tissue homogenate and permeabilized cells.
- SUIT-006: Very short coupling protocol with PM as NADH-linked substrates.
- SUIT-008: A protocol to evaluate NS-linked pathway in the OXPHOS and ET states.
- SUIT-004: Short version of RP1; without G, F and Gp.
- SUIT-012: Coupling control with NADH-linked substrates (PM and PGM) without Omy addition.
References
MitoPedia concepts: SUIT protocol, SUIT A, Find
MitoPedia methods:
Respirometry