Chabi 2019 MiP2019
| Generating reference values on mitochondrial respiration in permeabilized muscle fibers. |
Link: MiP2019
Chabi B, Ost M, Gama-Perez P, Dahdah N, Lemieux H, Holody CD, Carpenter RG, Tepp K, Puurand M, Kaambre T, Dubouchaud H, Cortade F, Pesta D, Calabria E, Casado M, Fernandez-Ortiz M, Acuna-Castroviejo D, Villena JA, Grefte S, Keijer J, O'Brien K, Sowton A, Murray AJ, Campbell MD, Marcinek DJ, Nollet E, Wuest R, Dayanidhi S, Gnaiger E, Doerrier C, Garcia-Roves PM (2019)
Event: MiP2019
Permeabilized muscle fibers (pfi) are widely used to assess mitochondrial (mt) respiratory function in skeletal muscle of various models in different physiological and pathological conditions. Facing the numerous data available for mt-respiration from the literature, it remains challenging to determine what the right values are for a specific respiratory protocol. Moreover, mt-respiration values are highly dependent on pfi preparation, which required good technical skills.
In the frame of COST Action MITOEAGLE, one of the objectives of WG2 is the generation of reference values for mitochondrial respirometry in permeabilized skeletal muscle sample preparations. The idea is that new researchers in the field follow a reference protocol and check if their values are in an acceptable range. This approach could serve to test researchers’ technical skills and therefore determine if they are proficient enough to perform their own experiments with confidence.
Sixteen international research groups participated to this study and received males (N=4) and females (N=4) C57BL/6J mice aged 14-16 weeks from the same provider. They performed permeabilized fibers from soleus muscle according to a common defined protocol.
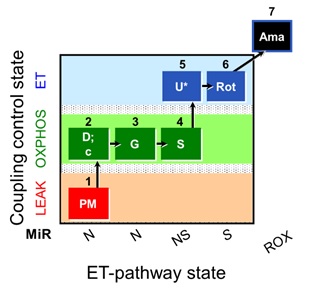
Mt-respiration was measured in respiration media MiR05-Kit following the substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration (SUIT) protocol SUIT-008_O2_pfi_D014 represented in Figure1 [1]. Chemicals were provided by each group.
Preliminary analyses of oxygen fluxes showed variability between the groups with median values for NS-OXPHOS capacity ranging from 116 to 335 pmol∙s-1∙mg tissue-1 (Figure 2). Sources of this variability are currently under investigation through the analysis of respiratory traces to define exclusion criteria as well as a questionnaire gathering technical information and operator skills.
This unique international study has the ambition to significantly contribute to the generation of a mt-database that will help research groups in the investigation of mitochondrial physiology and pathology. Moreover, such database will help in the harmonization of mt-respiratory protocols and the resolution of the reproducibility crisis in mt–research [2].
• Bioblast editor: Plangger M, Tindle-Solomon L
• O2k-Network Lab: FR Montpellier Wrutniak-Cabello C, DE Nuthetal Klaus S, ES Barcelona Garcia-Roves PM, CA Edmonton Lemieux H, EE Tallinn Kaambre T, DE Duesseldorf Roden M, IT Verona Calabria E, ES Valencia Casado Pinna M, ES Granada Acuna-Castroviejo D, NL Nijmegen Koopman WJH, NL Wageningen Keijer J, US AK Fairbanks O'Brien K, UK Cambridge Murray AJ, US WA Seattle Marcinek DJ, NL Amsterdam Nollet E, US IL Chicago Dayanidhi S, AT Innsbruck Oroboros, NL Amsterdam Wuest RC, DE Leipzip Ost M
Affiliations
- Chabi Béatrice(1), Ost M(2), Gama-Perez P(3), Dahdah N(3), Lemieux H(4), Holody CD(4), Carpenter RG(4), Tepp K(5), Puurand M(5), Kaambre T(5), Dubouchaud H(6), Cortade F(1), Pesta D(7,8), Calabria E(9), Casado M(10), Fernandez-Ortiz M(11), Acuña-Castroviejo D(11), Villena JA(12), Grefte S(13), Keijer J(13), O'Brien K(14), Sowton A(14), Murray AJ(14), Campbell MD(15), Marcinek DJ(15), Nollet E(16), Wüst R(16), Dayanidhi S(17), Gnaiger E(18,19), Doerrier C(18), Garcia-Roves PM(3)
- DMEM, INRA, Univ Montpellier, France
- German Inst Human Nutrition Potsdam-Rehbruecke, Potsdam, Germany
- Dept Physiological Sciences, Univ Barcelona Bellvitge Biomedical Research Inst (IDIBELL), Spain
- Fac Saint-Jean, Univ Alberta, Canada
- Lab Chemical Biology, National Inst Chemical Physics Biophysics, Tallinn, Estonia
- Lab Bioénergétique Fondamentale Appliquée, Univ Grenoble Alpes, INSERM, Grenoble, France
- Inst Clinical Diabetology, German Diabetes Center, Leibniz Center Diabetes Research Heinrich-Heine Univ Düsseldorf, Germany
- German Center Diabetes Research, Munich, Neuherberg, Germany
- Dept Neurological Movement Sciences, Univ Verona, Italy
- Dept Molecular Cellular Pathology Therapy, Inst Biomedicina de Valencia, Spain
- Biomedical Research Center, Univ Granada, Spain
- Metabolism Obesity Lab, Vall d’Hebron Research Inst, Barcelona, Spain
- Human Animal Physiology, Wageningen Univ, The Netherlands
- Dept Physiology, Development Neuroscience, Univ Cambridge, UK
- Dept Radiology, Univ Washington, South Lake Union, USA
- Dept Human Movement Sciences, Fac Behavioural Movement Sciences, Vrije Univ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
- Rehabilitation Inst Chicago, Feinberg School Medicine, Northwestern Univ, USA
- Oroboros Instruments, Innsbruck, Austria
- Dept Visceral, Transplant Thoracic Surgery, Daniel Swarovski Research Lab, Medical Univ Innsbruck, Austria
Figures
Figure 1. Substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration protocol (SUIT-008 O2 pfi D014). Sequential titrations and respiratory states. 1PM: NADH-pathway (N-pathway) in the presence of 5 mM pyruvate and 2 mM malate in the N-LEAK state. 2D: saturating ADP (N-OXPHOS state). 2c: 10 μM cytochrome c for evaluating the integrity of the outer mitochondrial membrane. 3G: 10 mM glutamate as an additional NADH-linked substrate (N-OXPHOS state). 4S: 10 mM succinate (NS-OXPHOS capacity). 5U: uncoupler titrations to evaluate the electron transfer- (ET-) capacity (NS-ET capacity). 6Rot: inhibition of CI by rotenone (S-ET capacity). 7Ama: inhibition of CIII by antimycin A (residual oxygen consumption, Rox). Oxygen concentration range in the experiment was maintained between 400-250 µM O2.
Figure 2. NS-OXPHOS capacity of permeabilized soleus muscle fibers. NS-OXPHOS capacity was measured in permeabilized soleus muscle fibers from male C57BL/6J mice by 16 research groups. Median with interquartile range show results from individual group with muscle fibers obtained from at least four soleus muscles.
References
- Lemieux H, Blier PU, Gnaiger E (2017) Remodeling pathway control of mitochondrial respiratory capacity by temperature in mouse heart: electron flow through the Q-junction in permeabilized fibers. Sci Rep 7:2840. SUIT-8_O2_pfi_D14
- Baker M (2016) 1,500 scientists lift the lid on reproducibility. Survey sheds light on the ‘crisis’ rocking research. Nature 533:452–4.
Labels: MiParea: Respiration, Instruments;methods
Organism: Mouse
Tissue;cell: Skeletal muscle
Preparation: Permeabilized tissue
Coupling state: LEAK, OXPHOS, ET
Pathway: N, S, NS, ROX
HRR: Oxygraph-2k